Week 4 of Configuration Management Systems course.
Course material: https://terokarvinen.com/2022/palvelinten-hallinta-2022p2/
Environment: VirtualBox VM running Debian 11 XFCE. VM has 4 GB of RAM and 40 GB of disk space.
a) Hello command!
Objective: Make a “Hello World” script available to the system and install it on all Salt minions. Include in your report the minions ‘ls -l /usr/local/bin/‘.
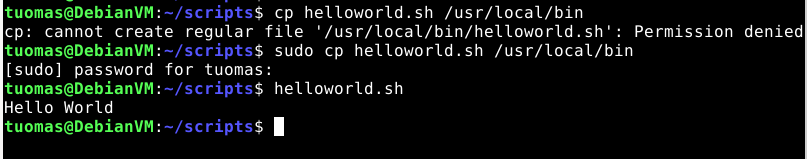
I started by running the command without a script.
$ echo "Hello World"
Hello WorldI created a file called helloworld.sh to ~/scripts.
$ micro helloworld.sh
$ cat helloworld.sh
#! /usr/bin/bash
echo "Hello World"I then copied the file to /usr/local/bin and tested it by typing helloworld.sh.
I created a new project directory under /srv/salt/
$ sudo mkdir helloshellI went to copy the script there and I noticed that I forgot to set execute permissions on the file. I fixed it and copied the script over.
$ cd ~/scripts
$ sudo chmod ugo+x helloworld.sh
$ sudo cp helloworld.sh /srv/salt/helloshell/I created an init.sls file. I checked helloworld.sh with the stat command to get its numeric permission information.
$ cd /srv/salt/helloshell
$ sudoedit init.sls
$ stat helloworld.sh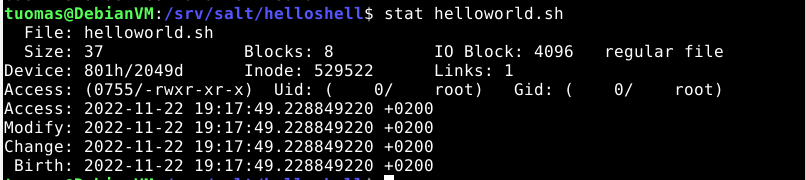
I then edited init.sls.
$ sudoedit init.sls
$ cat init.sls
/usr/local/bin/helloworld.sh:
file.managed:
- source: salt://helloshell/helloworld.sh
- mode: 755Because I have the salt minion installed locally on the same machine, I deleted the helloworld.sh script from /usr/local/bin before running the Salt code.
$ sudo rm /usr/local/bin/helloworld.shI added a test to the init.sls file.
$ cat init.sls
/usr/local/bin/helloworld.sh:
file.managed:
- source: salt://helloshell/helloworld.sh
- mode: 755
# Test
'ls -l /usr/local/bin/':
cmd.runI ran salt-call. The command worked and the ls line showed the right permissions.
$ sudo salt-call --local state.apply helloshell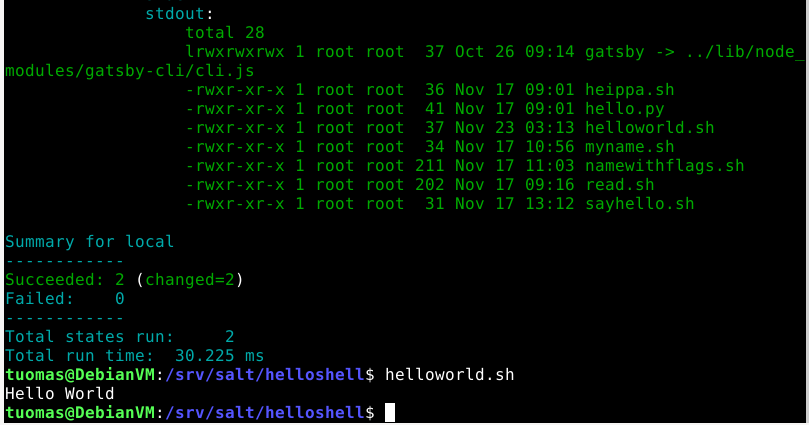
b) Whatsup.sh
Objective: Make a script available to the system that outputs current information. Install it to all Salt minions. Tips: You can show date, weather, system, network or other data.
Creating the script
I tested some commands I found through Google searches (sources: Tecmint, Ostechnix, Wrrt.in, Cyberciti):
# Show date & time
$ date
# Show system info
$ uname -a
# Show weather info
$ curl wttr.in/Helsinki?format=4
# Show network info. Needs tcpdump installed.
$ tcpdump --list-interfacesI created a file called showinfo.sh to ~/scripts.
$ cd ~/scripts
$ micro showinfo.shI gave execute permissions to all users.
$ sudo chmod ugo+x showinfo.shI added all the commands to the script, testing the functionality before adding the next one by running bash showinfo.sh.
$ cat showinfo.sh
#! /usr/bin/bash
echo "DATE AND TIME:" && date
echo " "
echo "SYSTEM INFO:" && uname -a
echo " "
echo "WEATHER INFO:" && curl wttr.in/Helsinki?format=4
echo " "
echo "NETWORK INTERFACES:" && tcpdump --list-interfaces(Source used: Preferred method to echo a blank line)
I ran the script.
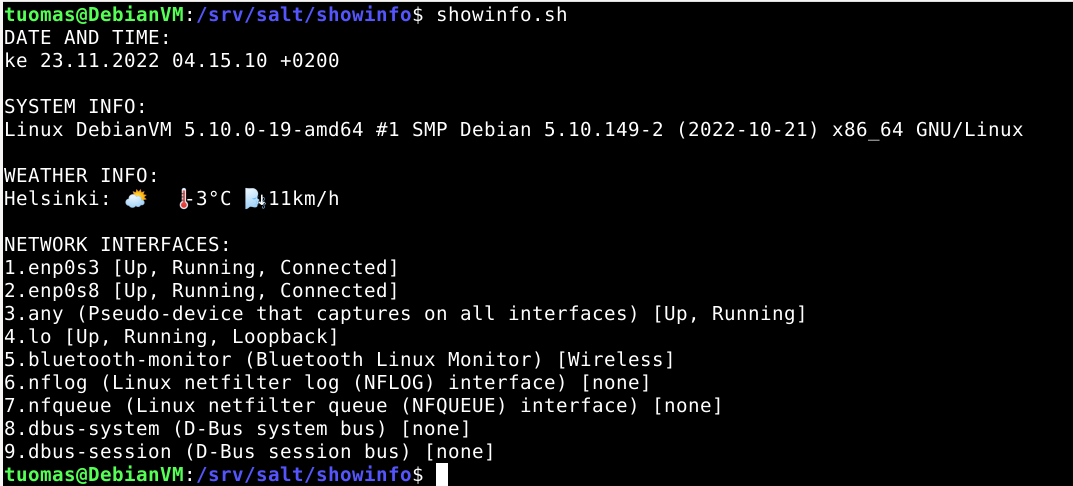
$ bash showinfo.sh
DATE AND TIME:
ke 23.11.2022 03.54.14 +0200
SYSTEM INFO:
Linux DebianVM 5.10.0-19-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.149-2 (2022-10-21) x86_64 GNU/Linux
WEATHER INFO:
Helsinki: ⛅️ 🌡️-3°C 🌬️↓11km/h
NETWORK INTERFACES:
1.enp0s3 [Up, Running, Connected]
2.enp0s8 [Up, Running, Connected]
3.any (Pseudo-device that captures on all interfaces) [Up, Running]
4.lo [Up, Running, Loopback]
5.bluetooth-monitor (Bluetooth Linux Monitor) [Wireless]
6.nflog (Linux netfilter log (NFLOG) interface) [none]
7.nfqueue (Linux netfilter queue (NFQUEUE) interface) [none]
8.dbus-system (D-Bus system bus) [none]
9.dbus-session (D-Bus session bus) [none]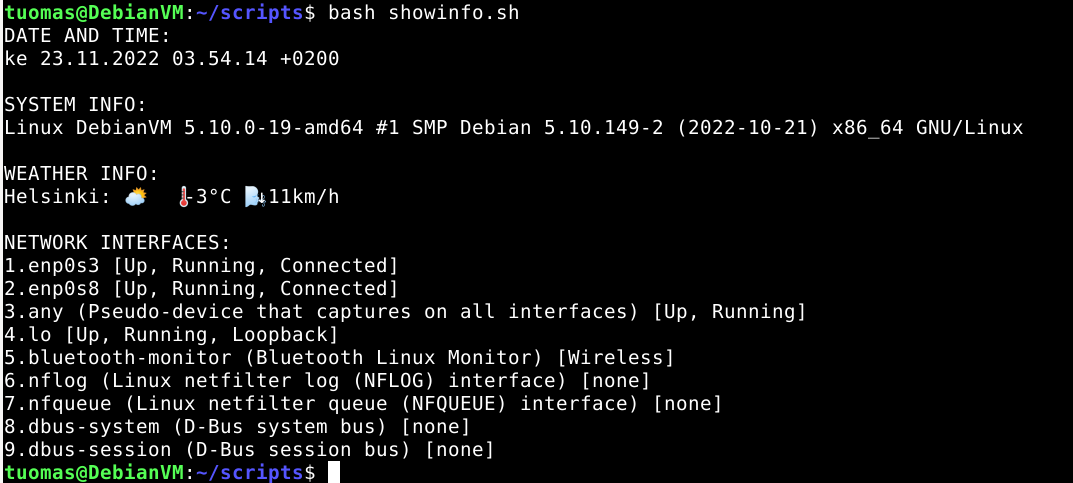
Creating Salt file
I created a new project directory under /srv/salt/.
$ sudo mkdir showinfo
$ cd showinfo/I copied the script to the Salt project.
$ sudo cp ~/scripts/showinfo.sh .I checked the right numerical permission. I saw that it was 755.
$ stat showinfo.sh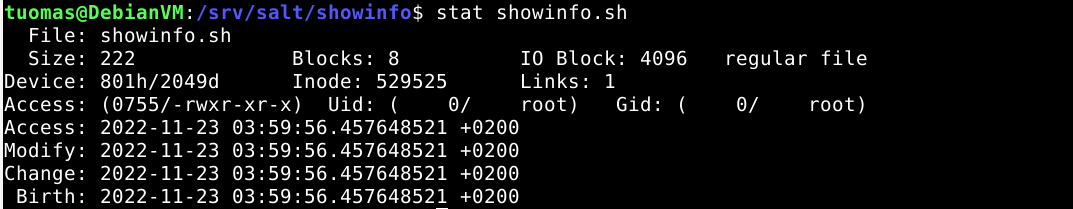
I created the init.sls file.
$ sudoedit init.sls
$ cat init.sls
tcpdump:
pkg.installed
/usr/local/bin/:
file.managed:
- source: salt://showinfo/showinfo.sh
- mode: 755
# Test
'ls -l /usr/local/bin/':
cmd.runI ran the Salt file with salt-call but there was an error with creating the script file. I typed the file location wrong.
$ sudo salt-call --local state.apply showinfo ID: /usr/local/bin/
Function: file.managed
Result: False
Comment: Specified target /usr/local/bin/ is a directory
Started: 04:08:00.711920
Duration: 2.367 ms
Changes: 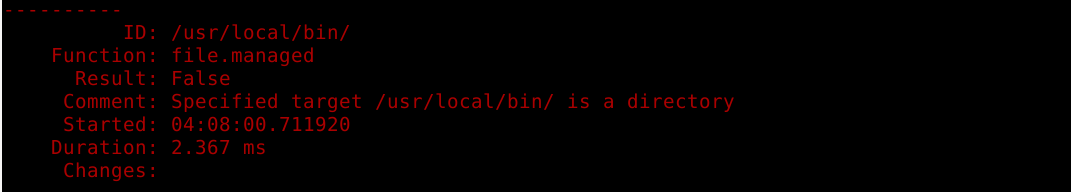
I fixed the code.
# Old
/usr/local/bin/:
# New
/usr/local/bin/showinfo.sh:I ran the command again. Now it worked.
$ sudo salt-call --local state.apply showinfo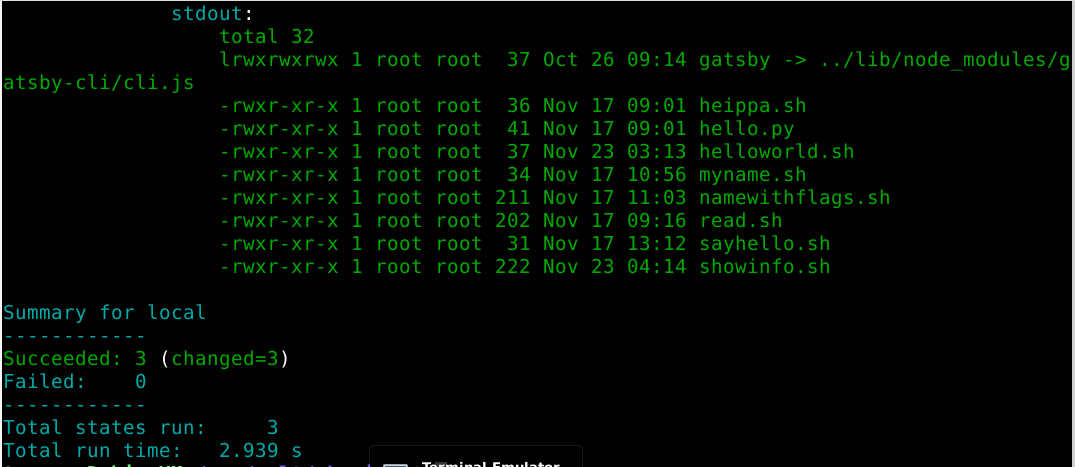
c) Hello.py
Objective: Create a script using Python and make it available to the system. Install it on Salt minions. A “Hello World” is sufficient. As Shebang use ”#!/usr/bin/python3”.
I created a new script called hellotest.py to ~/scripts.
$ cd ~/scripts
$ micro hellotest.py
$ cat hellotest.py
#! /usr/bin/python3
print('Hello World')I set execute permissions for everyone.
$ sudo chmod ugo+x hellotest.pyI tested the script by running it with python3.
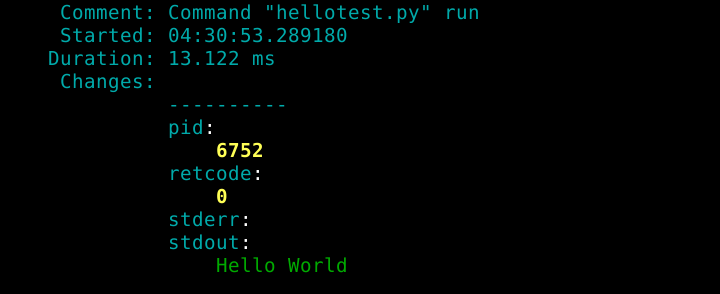
$ python3 hellotest.py
Hello World
I created a new Salt project under /srv/salt/.
$ cd /srv/salt
$ sudo mkdir hellopy
$ cd hellopyI copied the script to the Salt project.
$ sudo cp ~/scripts/hellotest.py .I checked the right permissions for the script with stat.
$ stat hellotest.pyI created an init.sls file. I added a test to run the script through Salt rather than testing it myself afterwards.
$ sudoedit init.sls
$ cat init.sls
/usr/local/bin/hellotest.py:
file.managed:
- source: salt://hellopy/hellotest.py
- mode: 755
# Test
'ls -l /usr/local/bin/':
cmd.run
'hellotest.py':
cmd.runI applied the Salt states.
$ sudo salt-call --local state.apply hellopy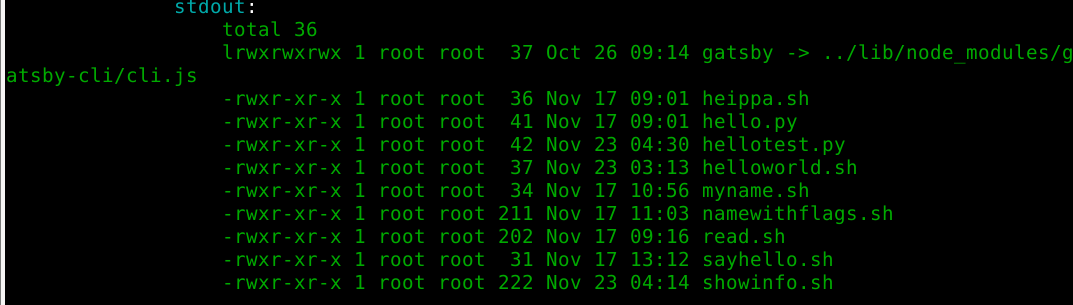
d) Lazy scripting
Objective: Create a directory for scripts and copy all contents to minions.
I created two new scripts to ~/scripts.
$ cd ~/scripts
# SCRIPT 1
$ micro hello-a.sh
$ cat hello-a.sh
#! /usr/bin/bash
echo "Hello "
# SCRIPT 2
$ micro hello-b.sh
$ cat hello-b.sh
#! /usr/bin/bash
echo "World"I gave both of them execute permissions for all.
$ sudo chmod ugo+x hello-a.sh hello-b.shI created a new Salt project under /srv/salt/.
$ cd /srv/salt
$ sudo mkdir hellotwiceI created another directory called scripts under hellotwice/.
$ sudo mkdir scriptsI copied the scripts to this new directory. (source: Copy multiple files using cp)
$ sudo cp ~/scripts/hello-a.sh ~/scripts/hello-b.sh scripts/I checked the permissions.
$ stat scripts/hello-a.shI created an init.sls file.
$ sudoedit init.sls
$ cat init.sls
/usr/local/bin/:
file.recurse:
- source: salt://hellotwice/scripts/
- file_mode: 755
# Test
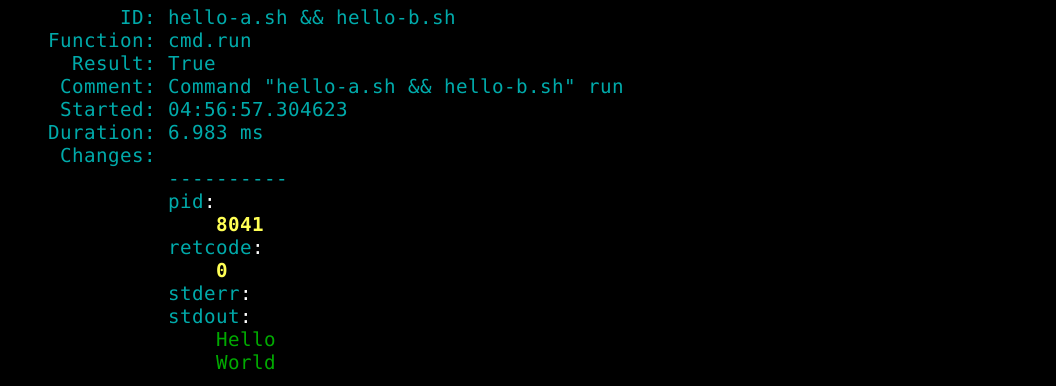
'ls -l /usr/local/bin/':
cmd.run
'hello-a.sh && hello-b.sh':
cmd.run(Source: salt-call --local sys.state_doc file.recurse)
I applied the Salt states. All commands worked.
$ sudo salt-call --local state.apply hellotwice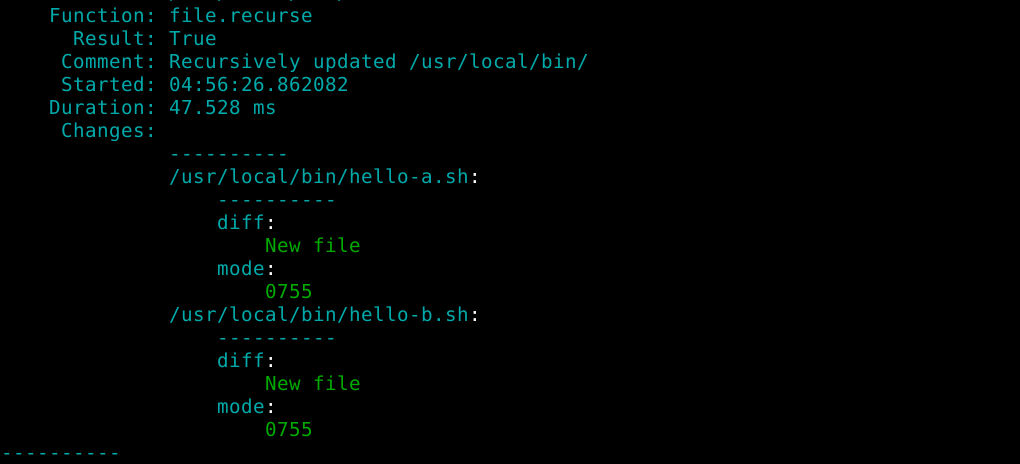
e) Intel
Objective: Find three course projects from previous courses. Summarize the projects, add source reference to the original report.
Project #1 - Samba
This project installs Samba, copies a Samba configuration file to /etc/samba/, and starts the Samba service when the configuration file gets updated. It also creates a directory called /Tiedostot with a Hello World .txt file in it.
The project doesn’t include the Samba configuration file so it can’t be run out of the box.
Project #2 - Basic setup for new Machines
This project installs and configures many applications including UFW firewall, Apache, and SSH.
Project #3 - LEMP stack
This project installs the LEMP stack which stands for Linux, Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP. For Nginx the project makes configurations to /etc/hosts/ and /etc/nginx/. It also copies HTML templates to /var/www/. For MariaDB the project runs a script that does some security related actions via SQL commands. It also creates a database and adds some content to it. For PHP the project copies a PHP file to /var/www/.
f) Read, don’t trust
Objective: Try out one of the modules you found in the previous exercise. This is infrastructure-as-code so no trust is needed. You can read what you are about to run right from the source code.
I decided to try out the LEMP stack project. I installed a new Debian Xfce VM.
I started by installing Wget.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install wgetI downloaded run.sh from GitHub.
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/santtuhurri/lemphelper/main/run.shI ran the script. It installed the Salt modules under /srv/salt/.
$ bash run.shI ran the Salt states.
$ sudo salt-call --local state.apply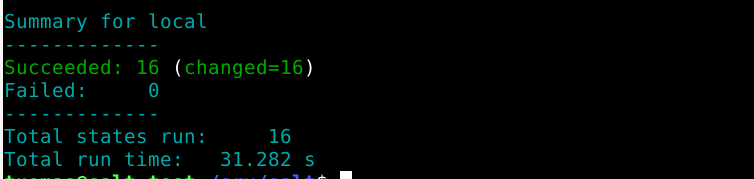
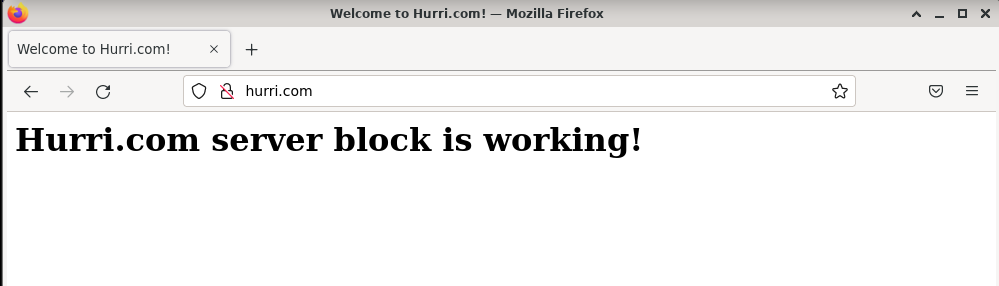
I tested Nginx by going to hurri.com in Firefox.
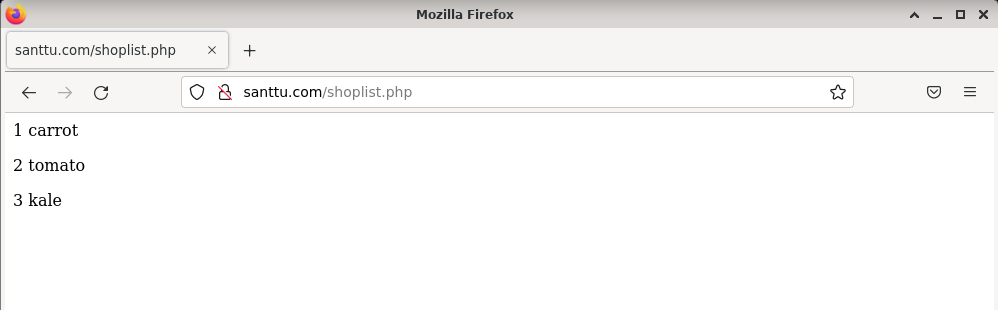
The PHP page that gets data from MariaDB also worked.
Sources
- Tero Karvinen: https://terokarvinen.com/2022/palvelinten-hallinta-2022p2/
- Tecmint: https://www.tecmint.com/commands-to-collect-system-and-hardware-information-in-linux/
- Ostechnix: https://ostechnix.com/check-weather-details-command-line-linux/
- Wrrt.in: https://github.com/chubin/wttr.in
- Cyberciti: https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-list-network-interfaces-names-command/
- Stackoverflow: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37052899/what-is-the-preferred-method-to-echo-a-blank-line-in-a-shell-script
- Linuxhint: https://linuxhint.com/copy-multiple-files-using-cp-linux/
- Project 1: https://neljakultakalaa.wordpress.com/2022/05/12/h7-oma-moduli/
- Project 2: https://github.com/nicotuoreniemi/Project-H7
- Project 3: https://github.com/santtuhurri/lemphelper